Dental Bridge
Dental bridges literally bridge the gap created by one or more missing teeth.
A bridge is made up of two or more crowns for the teeth on either side of the gap, these two or more anchoring teeth are called abutment teeth and a false tooth/teeth in between. These false teeth are called pontics and can be made from gold, alloys, porcelain, or a combination of these materials. Dental bridges are supported by natural teeth or implants.
What Are the Benefits of Dental Bridges?
- Restore your smile
- Restore the ability to properly chew and speak
- Maintain the shape of your face
- Distribute the forces in your bite properly by replacing missing teeth
- Prevent remaining teeth from drifting out of position
- What Types of Dental Bridges Are Available?
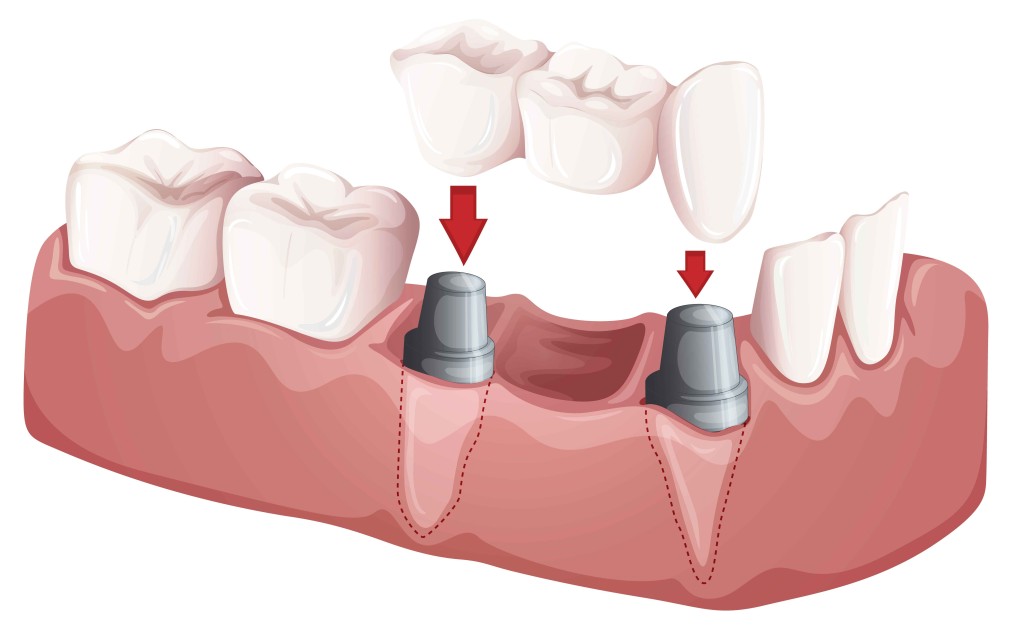
There are three main types of dental bridges:
Traditional bridges involve creating a crown for the tooth or implant on either side of the missing tooth, with a pontic in between. Traditional bridges are the most common type of bridge and are made of either porcelain fused to metal or ceramics.
Cantilever bridges are used when there are adjacent teeth on only one side of the missing tooth or teeth. This is not very common any more and is not recommended in the back of the mouth where it can put too much force on other teeth and damage them.
Maryland bonded bridges (also called a resin-bonded bridge or a Maryland bridge) are made of porcelain, porcelain fused to metal, or plastic teeth and gums supported by a metal or porcelain framework. Metal or porcelain wings on each side of the bridge are bonded to your existing teeth.
Process for Getting a Dental Bridge?
During the first visit for getting a dental bridge, the abutment teeth are prepared. Preparation involves re-contouring these teeth by removing a portion of enamel to allow room for a crown to be placed over them. Next, impressions of the teeth are made, which serve as a model from which the bridge, pontic, and crowns will be made by a dental lab. Your dentist will make a temporary bridge to wear to protect the exposed teeth and gums while the bridge is being made.
During the second visit, your temporary bridge will be removed and the new porcelain or metal bridge will be checked and adjusted, as necessary, to achieve a proper fit. Multiple visits may be required to check the fit of the metal framework and bite. This is dependent on each individual's case. If the dental bridge is a fixed bridge, your dentist may temporarily cement it in place for a couple of weeks to make sure it is fitting properly. After a couple weeks, the bridge is cemented into place.
How Do I Care for a Bridge?
It is important to keep remaining teeth healthy and strong as the success of the bridge (depending on the type selected) depends on the solid foundation offered by the surrounding teeth. Brushing twice a day and flossing and using an antiseptic mouthwash daily help prevent tooth decay and gum disease that can lead to tooth loss. Your dentist or dental hygienist can demonstrate how to properly brush and floss teeth. Keeping a regular cleaning schedule will help diagnose problems at an early stage when treatment has a better prognosis. Selecting a balanced diet for proper nutrition is also important
